- 0. 小结
- 3. Number of Parameters
- 7. 2-Layer Neural Network
- 8. Quiz: TensorFlow ReLu
- 11. Backprop 反向传播
- 12. Deep Neural Network in TensorFlow
- 13. Training a Deep Learning Network
- 14. Save and Restore TensorFlow Models
- 15. Fine tuning
- 18. Regularization
- 19. Dropout
- 21. Quiz: TensorFlow Dropout
- 22. Quiz 2: TensorFlow Dropout
0. 小结
本章主要介绍了一些优化深度学习的方法,以及在TensorFlow中如何实现:
- 什么是ReLU函数,以及如何用TensorFlow实现
- 反向传播
- TensorFlow中的深度神经网络,包括如何初始化,定义权重,以及各种超参数等
- 如何在TensorFlow中保存变量,保存模型称为本地文件,并在下一次使用时load数据
- 如何防止过拟合,权值衰减在TensorFlow中如何实施
- 同样为了防止过拟合,使用Dropout方法,了解Dropout在TensorFlow中如何实施
3. Number of Parameters
计算下面网络中的参数个数:

上面的参数,有权重和偏置,权重(input,label),偏置(label,)
= size of W + size of b
= 28x28x10 + 10
= 7850
可以参考如下代码:
n_features = 3
n_labels = 5
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal((n_features, n_labels)))
bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(n_labels))
7. 2-Layer Neural Network

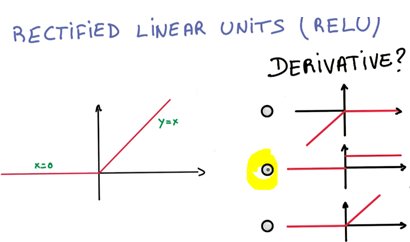
ReLU 是个非线性函数,当x大于0时,y等于x;否则y为0,该函数的导数如下图:
- 第一层由输入x和其对应的权重w及偏置bias构成,结果经由ReLU函数,传递给下一层神经网络。
- 第二层由上一层的中间结果,以及该层的权重w和偏置bias构成,计算出来的结果,最终传递给激活函数如softmax函数,计算出概率。
8. Quiz: TensorFlow ReLu
ReLU函数(f(x) = max(0, x)),也是一种激活函数,它在TensorFlow中用 tf.nn.relu()来定义,示例代码如下:
# Hidden Layer with ReLU activation function
hidden_layer = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, hidden_weights), hidden_biases)
hidden_layer = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer)
output = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer, output_weights), output_biases)
上面的代码:
- 将 tf.nn.relu() 应用到了 hidden_layer 隐藏层。
- 添加了一个新的层output layer,output layer的输入数据是前一层hidden_layer的输出(非线性Relu函数处理后的)
In this quiz, you’ll use TensorFlow’s ReLU function to turn the linear model below into a nonlinear model.
代码如下:
# Solution is available in the other "solution.py" tab
import tensorflow as tf
output = None
hidden_layer_weights = [
[0.1, 0.2, 0.4],
[0.4, 0.6, 0.6],
[0.5, 0.9, 0.1],
[0.8, 0.2, 0.8]]
out_weights = [
[0.1, 0.6],
[0.2, 0.1],
[0.7, 0.9]]
# Weights and biases
weights = [
tf.Variable(hidden_layer_weights),
tf.Variable(out_weights)]
biases = [
tf.Variable(tf.zeros(3)),
tf.Variable(tf.zeros(2))]
# Input
features = tf.Variable([[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0], [-1.0, -2.0, -3.0, -4.0], [11.0, 12.0, 13.0, 14.0]])
# TODO: Create Model
hidden_layer = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, weights[0]), biases[0])
hidden_layer = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer)
output = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer, weights[1]), biases[1])
# TODO: save and print session results on a variable named "output"
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Run the tf.constant operation in the session
sess.run(init)
result = sess.run(output)
print(result)
输出结果如下:
[[ 5.11000013 8.44000053]
[ 0. 0. ]
[ 24.01000214 38.23999786]]
11. Backprop 反向传播

这部分就是误差反向传播法的内容,详细要参考这里。
12. Deep Neural Network in TensorFlow
12.1 示例代码:
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(".", one_hot=True, reshape=False)
import tensorflow as tf
# Parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 20
batch_size = 128 # Decrease batch size if you don't have enough memory
display_step = 1
n_input = 784 # MNIST data input (img shape: 28*28)
n_classes = 10 # MNIST total classes (0-9 digits)
n_hidden_layer = 256 # layer number of features
# Store layers weight & bias
weights = {
'hidden_layer': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input, n_hidden_layer])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_layer, n_classes]))
}
biases = {
'hidden_layer': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_layer])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
}
# tf Graph input
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 28, 28, 1])
y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, n_classes])
x_flat = tf.reshape(x, [-1, n_input])
# Hidden layer with RELU activation
layer_1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_flat, weights['hidden_layer']), biases['hidden_layer'])
layer_1 = tf.nn.relu(layer_1)
# Output layer with linear activation
logits = tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['out']) + biases['out']
# Define loss and optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# Initializing the variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Launch the graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
# Training cycle
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
# Loop over all batches
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
# Run optimization op (backprop) and cost op (to get loss value)
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
# Display logs per epoch step
if epoch % display_step == 0:
c = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch+1), "cost=", \
"{:.9f}".format(c))
print("Optimization Finished!")
# Test model
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
# Calculate accuracy
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
# Decrease test_size if you don't have enough memory
test_size = 256
print("Accuracy:", accuracy.eval({x: mnist.test.images[:test_size], y: mnist.test.labels[:test_size]}))
12.2 代码解析
- 使用TensorFlow提供的MNIST数据,已经做好了batch和one-hot编码处理:
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(".", one_hot=True, reshape=False)
- Learning Parameters
定义各类超参数:
import tensorflow as tf
# Parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 20
batch_size = 128 # Decrease batch size if you don't have enough memory
display_step = 1
n_input = 784 # MNIST data input (img shape: 28*28)
n_classes = 10 # MNIST total classes (0-9 digits)
- Hidden Layer Parameters
定义隐藏层上的神经元数量:
n_hidden_layer = 256 # layer number of features
- Weights and Biases 权重和偏置
这里只有两层神经网络,所有只有hidden_layer和out的权重及偏置
# Store layers weight & bias
weights = {
'hidden_layer': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input, n_hidden_layer])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_layer, n_classes]))
}
biases = {
'hidden_layer': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_layer])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
}
- input 输入数据
# tf Graph input
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 28, 28, 1])
y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, n_classes])
x_flat = tf.reshape(x, [-1, n_input])
需要将28*28的单通道数据([None, 28, 28, 1]),通过reshape转换成一行数据,一行中有784个像素点数据。
- Multilayer Perceptron 多层感知

下面代码先计算xW+b,然后将其传递给ReLU层,最后传递给下一个xW+b,得到最后的logits layer:
# Hidden layer with RELU activation
layer_1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_flat, weights['hidden_layer']),\
biases['hidden_layer'])
layer_1 = tf.nn.relu(layer_1)
# Output layer with linear activation
logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1, weights['out']), biases['out'])
- Optimizer 优化器
# Define loss and optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(\
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)\
.minimize(cost)
- session
TensorFlow中提供的MNIST library库,能够批量接收数据集,使用mnist.train.next_batch()函数返回训练数据的一个子集subset。
# Initializing the variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Launch the graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
# Training cycle
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
# Loop over all batches
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
# Run optimization op (backprop) and cost op (to get loss value)
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
13. Training a Deep Learning Network
更深的模型,往往会呈现出层次化的结构,比如第一层学习到线条,第二层有形状,第三层逐渐抽象成人脸的形状,逐步获取数据中的抽象内容,这正是深度学习所期待的。

类似的描述,在CNN中也有,参考6.2 基于分层结构的信息提取
14. Save and Restore TensorFlow Models
训练一个模型往往也要几个小时时间,一段中断了TensorFlow的session,那可能会丢失训练好的权重和偏置等数据。
通过TensorFlow的函数tf.train.Saver,能将各种tf.Variable变量保存到本地文件中。
14.1 Saving Variables
下面的代码中,保存了两个变量 weights and bias 。
import tensorflow as tf
# The file path to save the data
save_file = './model.ckpt'
# Two Tensor Variables: weights and bias
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([2, 3]))
bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3]))
# Class used to save and/or restore Tensor Variables
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Initialize all the Variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# Show the values of weights and bias
print('Weights:')
print(sess.run(weights))
print('Bias:')
print(sess.run(bias))
# Save the model
saver.save(sess, save_file)
Weights:
[[ 0.74129212 1.16585362 0.18823986]
[ 0.84469903 -0.30504367 -0.9390443 ]]
Bias:
[-0.0300845 0.12080105 0.38587224]
最后在本地的文件夹中,有model.ckpt.meta文件被保存。
14.2 Loading Variables
将保存好的数据load到新的model中:
# Remove the previous weights and bias
tf.reset_default_graph()
# Two Variables: weights and bias
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([2, 3]))
bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3]))
# Class used to save and/or restore Tensor Variables
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Load the weights and bias
saver.restore(sess, save_file)
# Show the values of weights and bias
print('Weight:')
print(sess.run(weights))
print('Bias:')
print(sess.run(bias))
INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from ./model.ckpt
Weight:
[[ 0.74129212 1.16585362 0.18823986]
[ 0.84469903 -0.30504367 -0.9390443 ]]
Bias:
[-0.0300845 0.12080105 0.38587224]
可以看到上面得到的数据,以前一个保存的时候是一样的,如果将代码修改为:
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Load the weights and bias
#saver.restore(sess, save_file)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# Show the values of weights and bias
print('Weight:')
print(sess.run(weights))
print('Bias:')
print(sess.run(bias))
即不使用保存的数据,那么得到的结果不同:
Weight:
[[ 0.51144725 0.18832855 0.00272263]
[ 0.05852098 -0.44724768 -0.96787697]]
Bias:
[-0.05925143 -1.33713555 0.32981932]
14.3 Save a Trained Model
训练一个模型,并保存其权重值:
- 先新建一个模型
# Remove previous Tensors and Operations
tf.reset_default_graph()
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import numpy as np
learning_rate = 0.001
n_input = 784 # MNIST data input (img shape: 28*28)
n_classes = 10 # MNIST total classes (0-9 digits)
# Import MNIST data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('.', one_hot=True)
# Features and Labels
features = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input])
labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes])
# Weights & bias
weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input, n_classes]))
bias = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
# Logits - xW + b
logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, weights), bias)
# Define loss and optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(\
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=labels))
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)\
.minimize(cost)
# Calculate accuracy
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(labels, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
- 再训练一个模型,并保存其权重:
import math
save_file = './train_model.ckpt'
batch_size = 128
n_epochs = 100
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# Launch the graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# Training cycle
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
total_batch = math.ceil(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
# Loop over all batches
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_features, batch_labels = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(
optimizer,
feed_dict={features: batch_features, labels: batch_labels})
# Print status for every 10 epochs
if epoch % 10 == 0:
valid_accuracy = sess.run(
accuracy,
feed_dict={
features: mnist.validation.images,
labels: mnist.validation.labels})
print('Epoch {:<3} - Validation Accuracy: {}'.format(
epoch,
valid_accuracy))
# Save the model
saver.save(sess, save_file)
print('Trained Model Saved.')
14.4 Load a Trained Model
load一个训练好的模型:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# Launch the graph
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, save_file)
test_accuracy = sess.run(
accuracy,
feed_dict={features: mnist.test.images, labels: mnist.test.labels})
print('Test Accuracy: {}'.format(test_accuracy))
15. Fine tuning
将保存好的变量,直接load到一个修改后的model中,会产生错误。
15.1 Naming Error
import tensorflow as tf
# Remove the previous weights and bias
tf.reset_default_graph()
save_file = 'model.ckpt'
# Two Tensor Variables: weights and bias
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([2, 3]))
bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3]))
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# Print the name of Weights and Bias
print('Save Weights: {}'.format(weights.name))
print('Save Bias: {}'.format(bias.name))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver.save(sess, save_file)
# Remove the previous weights and bias
tf.reset_default_graph()
# Two Variables: weights and bias
bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3]))
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([2, 3]))
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# Print the name of Weights and Bias
print('Load Weights: {}'.format(weights.name))
print('Load Bias: {}'.format(bias.name))
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Load the weights and bias - ERROR
saver.restore(sess, save_file)
上面weights和bias的name,与之前保存的model时不同,所以出现了下面的错误:
Assign requires shapes of both tensors to match
修改后代码如下,添加了name属性的指定:
import tensorflow as tf
tf.reset_default_graph()
save_file = 'model.ckpt'
# Two Tensor Variables: weights and bias
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([2, 3]), name='weights_0')
bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3]), name='bias_0')
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# Print the name of Weights and Bias
print('Save Weights: {}'.format(weights.name))
print('Save Bias: {}'.format(bias.name))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver.save(sess, save_file)
# Remove the previous weights and bias
tf.reset_default_graph()
# Two Variables: weights and bias
bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3]), name='bias_0')
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([2, 3]) ,name='weights_0')
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# Print the name of Weights and Bias
print('Load Weights: {}'.format(weights.name))
print('Load Bias: {}'.format(bias.name))
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Load the weights and bias - No Error
saver.restore(sess, save_file)
print('Loaded Weights and Bias successfully.')
18. Regularization
本节关于如何防止过拟合,可以参考 正则化
通常有两种方式:
- Early Termination: 当发现性能不再上升时,就停止训练
- L2 Regularization: L2正则化,惩罚那些权重高的,即这里的权值衰减
19. Dropout
参考 dropout,随机删除一些流经激活函数的数据。
21. Quiz: TensorFlow Dropout
Dropout是一种防止过拟合的方式,它随机删除一些神经元,如下图:

在TensorFlow中,通过函数tf.nn.dropout()可以实现dropout,示例代码如下:
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # probability to keep units
hidden_layer = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, weights[0]), biases[0])
hidden_layer = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer)
hidden_layer = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer, keep_prob)
logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer, weights[1]), biases[1])
The tf.nn.dropout() function takes in two parameters:
- hidden_layer: the tensor to which you would like to apply dropout
- keep_prob: the probability of keeping (i.e. not dropping) any given unit
通过keep_prob控制要drop的量,一般在训练的时候,设置为0.5,而在test的时候,要max model的作用,设置为1,即不drop任何神经元。
下面是一段示例代码:
...
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # probability to keep units
hidden_layer = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, weights[0]), biases[0])
hidden_layer = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer)
hidden_layer = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer, keep_prob)
logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer, weights[1]), biases[1])
...
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for epoch_i in range(epochs):
for batch_i in range(batches):
....
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={
features: batch_features,
labels: batch_labels,
keep_prob: 0.5})
validation_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={
features: test_features,
labels: test_labels,
keep_prob: 1.0})
22. Quiz 2: TensorFlow Dropout
下面将实际使用dropout,代码如下:
# Quiz Solution
# Note: You can't run code in this tab
import tensorflow as tf
hidden_layer_weights = [
[0.1, 0.2, 0.4],
[0.4, 0.6, 0.6],
[0.5, 0.9, 0.1],
[0.8, 0.2, 0.8]]
out_weights = [
[0.1, 0.6],
[0.2, 0.1],
[0.7, 0.9]]
# set random seed
tf.set_random_seed(123456)
# Weights and biases
weights = [
tf.Variable(hidden_layer_weights),
tf.Variable(out_weights)]
biases = [
tf.Variable(tf.zeros(3)),
tf.Variable(tf.zeros(2))]
# Input
features = tf.Variable([[0.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0], [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4], [11.0, 12.0, 13.0, 14.0]])
# TODO: Create Model with Dropout
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
hidden_layer = tf.add(tf.matmul(features, weights[0]), biases[0])
hidden_layer = tf.nn.relu(hidden_layer)
hidden_layer = tf.nn.dropout(hidden_layer, keep_prob)
logits = tf.add(tf.matmul(hidden_layer, weights[1]), biases[1])
# TODO: save and print session results as variable named "output"
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
output = sess.run(logits, feed_dict={keep_prob: 0.5})
print(output)
输出结果如下:
[[ 9.55999947 16. ]
[ 0.11200001 0.67200011]
[ 43.30000305 48.15999985]]